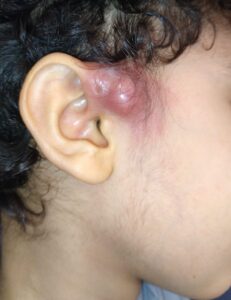
Bambino affetto da cisti preauricolare (primo arco branchiale) infetta. Posteriormente alla cisti, davanti alla radice dell’elice, è possibile osservare lo sbocco del tramite fistoloso.

Bambino affetto da cisti preauricolare (primo arco branchiale) infetta. Posteriormente alla cisti, davanti alla radice dell’elice, è possibile osservare lo sbocco del tramite fistoloso.
The head impulse test is a clinical examination is very useful in the evaluation of patients with dizziness or balance deficit.
And’ a noninvasive test very quickly but not always easy to evaluate.
It asks the patient to fix a point in the vicinity of the eyes of the operator (the tip of the nose or a shirt button) and they make the patient's head of short, but very quickly to the right or left unpredictably.
Under normal conditions the brain uses information from the sight and the organ of balance and manages to keep the fixed pupils on target.
If the organ of balance does not work correctly, Turning her head to the side sick, the pupil will fail to stay on target and will tend to go sideways; later the brain realizes the mistake and fixes his gaze with a quick movement of the pupil (saccade).
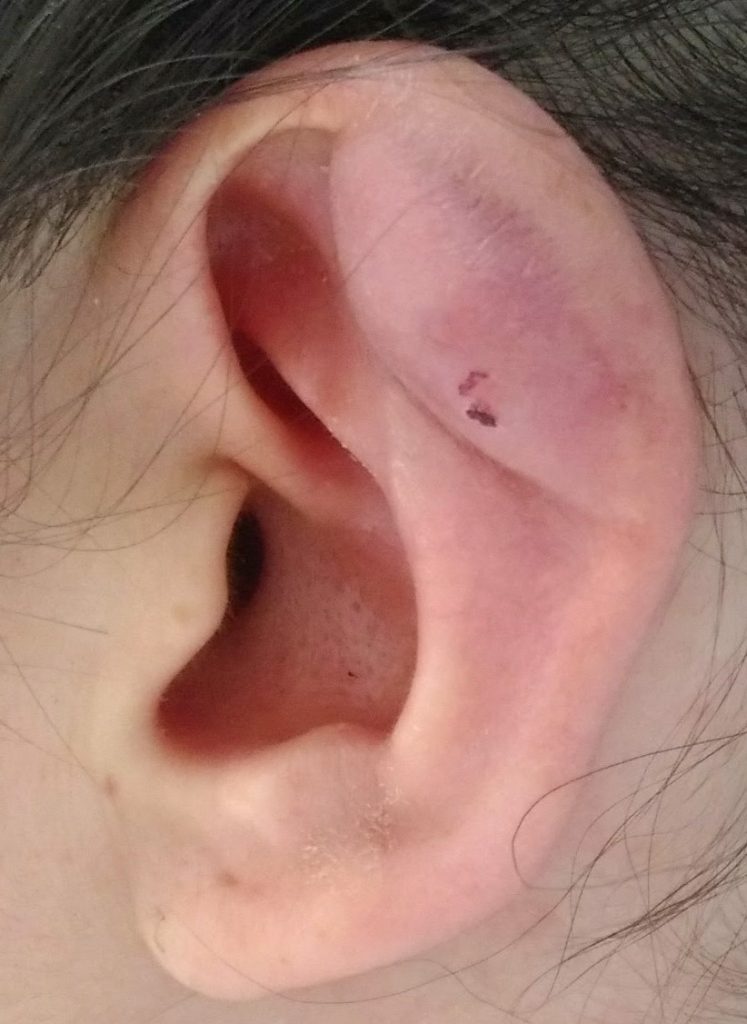
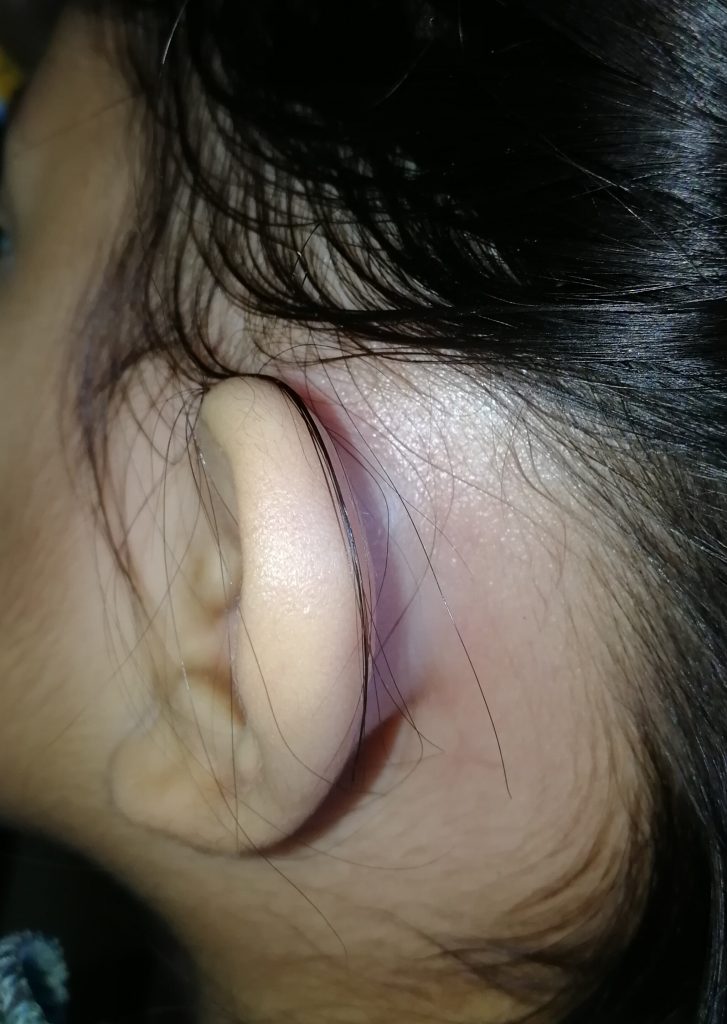
Trauma and foreign bodies can cause infections of the ear, If the pus can't escape outside can accumulate in the Hall, creating a swelling.
Sometimes an ear trauma can cause bleeding that accumulates in the Hall by creating a otoematoma, a swelling that look very similar to an abscess but in the absence of infectious processes.
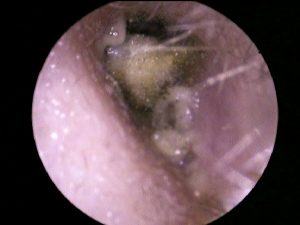
The mycotic otitis externa is an infection of the external ear canal from fungus that causes symptoms nuanced and often underestimated by the patient. May cause mild pain (ear pain), itching, hearing loss (hearing loss), sometimes tinnitus. Continue reading →
 The impedance is a quick review, painless and non-invasive way that easily allows to objectify the presence of fluid in the middle ear (payment endotimpanico), changes in air pressure in the middle ear and to assess the presence of stapedial reflexes. Continue reading →
The impedance is a quick review, painless and non-invasive way that easily allows to objectify the presence of fluid in the middle ear (payment endotimpanico), changes in air pressure in the middle ear and to assess the presence of stapedial reflexes. Continue reading →
For sudden hypoacusis means a decrease of hearing greater than 30 DB to tonal audiometric test covering at least 3 contiguous frequencies and occur in less than 3 days.
Patients experience a decrease in hearing or deafness that appears suddenly, upon waking or at any moment, almost always on one side and often associated with wheezing (Tinnitus), feeling of weight headset, noise distortion. Continue reading →
 I don't usually do terrorism. My personal opinion is that the physician is required to know all the possible complications, including the most recondite and serious but must communicate to the patient more realistic ones only, updating if necessary the patient as the clinical situation evolves.
I don't usually do terrorism. My personal opinion is that the physician is required to know all the possible complications, including the most recondite and serious but must communicate to the patient more realistic ones only, updating if necessary the patient as the clinical situation evolves.
Say to the family of a child 7 years with male all ’ ear from 1-2 days that could die is pure and simple terrorism. If after 7 GG important symptoms, in aggravation, do not make a therapy … then the risk life exists! Continue reading →
Movie showing the head shaking test positive, triggering important swing-right nystagmus
The term congenital nystagmus is an incessant movement of the eyes, commuter trend that is present from birth or the first weeks of life.
Unlike the nystagmus, pathologic found in vertiginous syndromes, are not recognizable quick phase and the slow phase of nystagmus.
The brain of affected subjects learn to exclude image determined by eye movement and get a stable image ’.
Scientific Association for
training, of care and solidarity
in Otolaryngology