L ’ dell ’ disease middle ear and hearing test procedure which determine hearing loss. The mechanisms of Otosclerosis are not completely known, seems to be a strong genetic component with a presumed autosomal dominant transmission mostly incomplete. L ’ Otosclerosis affects mainly women (with a report 2:1) and when life tends to involve both ears.
Ear and balance - 3. page
L ’ tone audiometric test
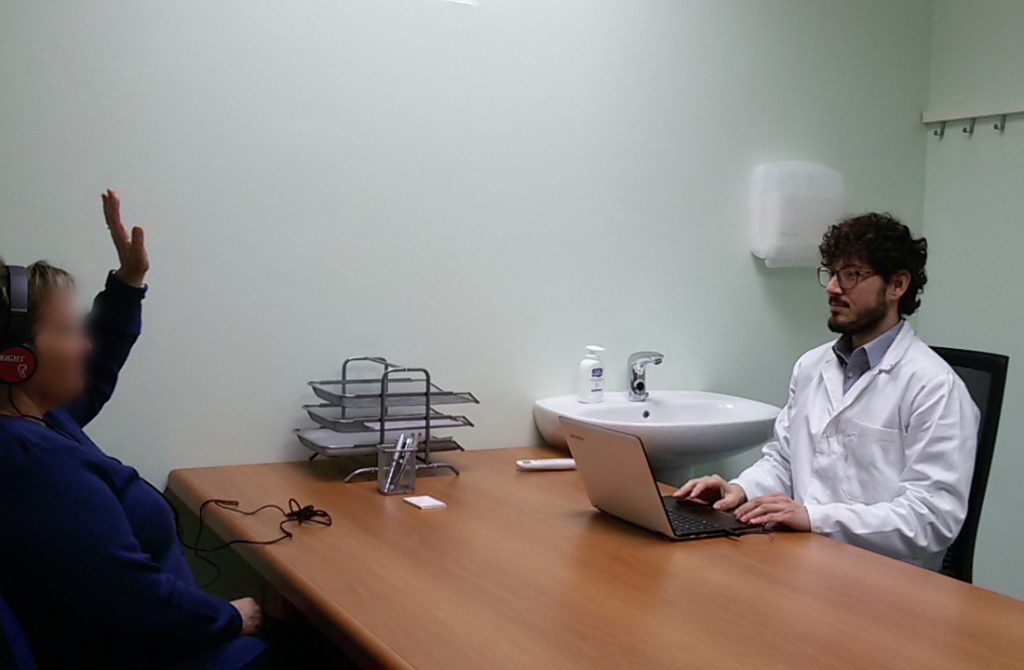 L ’ tonal audiometric allows decrease of hearing by quantifying ’ l ’ objectify extent of hearing loss and which frequencies being affected. And’ can also study separately the functionality of the auditory nerve and sound transmission system (outer ear, tympanic membrane, auditory ossicles and the middle ear).
L ’ tonal audiometric allows decrease of hearing by quantifying ’ l ’ objectify extent of hearing loss and which frequencies being affected. And’ can also study separately the functionality of the auditory nerve and sound transmission system (outer ear, tympanic membrane, auditory ossicles and the middle ear).
And’ a simple exam ’, non-invasive and short-lived.
The patient is placed in a quiet or soundproofed and are placed headphones through which are heard of pure tones (sounds with a specific frequency) a ’ intensity note. The patient is asked to report when it is able to hear sound. Is then marked on a path the minimum intensity at which the subject is able to hear the sounds, distinguishing the individual frequencies and two ears.
L ’ instability and dizziness
L ’ human being is able to sense its position in space by integrating information from dell ’ organ ’ balance which may (in ’ inner ear), from view, by ’ hearing, by feel and perception of the position of your body. All information is processed and processed by the central nervous system.
A disease that affects any of these steps may cause instability and Vertigo.
And’ first crucial to distinguish dizziness affecting the central nervous system (neurological diseases) dizziness of peripheral origin, ENT competence.
Continue reading
Videonistagmografia
 In healthy person, l ’ ’ organ of balance (vestibular system) It also plays a key role in ’ assist the brain in controlling eye movements so as not to lose the setting of an object despite abrupt head movements.
In healthy person, l ’ ’ organ of balance (vestibular system) It also plays a key role in ’ assist the brain in controlling eye movements so as not to lose the setting of an object despite abrupt head movements.
In pathology the vestibular system can cause abnormal eye movements called nystagmus.
L ’ careful evaluation of these movements is spontaneous that caused is essential to frame the dizziness and ’ instability. Being eye-movements controlled by the brain from the vestibular system it is important to try to exclude as much as possible, l ’ central task: It then tries to put the patient in a position not to see the ’ environment. To achieve this condition you can use goggles Frenzel with strongly miopizzanti that waste the patient lenses every visual reference.
L ’ technological evolution is represented by videonistagmografia: a mask with camera with Infrared Illuminator. Once worn the patient will be in complete darkness while l ’ examiner will investigate and possibly record the movements of eyes evaluating in a monitor.
Registering with videonistagmografia Rotary nystagmus, physiologic in healthy person Continue reading
Tinnitus and sound enrichment ’
Tinnitus (or tinnitus) are sounds perceived by patients but not in ’ environment. Their nature can relate to organic diseases (Otosclerosis, acoustic trauma, dell ’ VII acoustic nerve neurinoma, sudden hearing loss, hearing loss ototoxic agents, neurological diseases …) or, in most cases, from an unidentifiable cause.
Tinnitus involve a large number of subjects (until 15-18% of the population), may be constant or intermittent, unilateral or bilateral.
L ’ Tinnitus can be acute or severe tone, mild or very high. Can be very annoying, especially in quiet environments, situation in which it is perceived more.
Tinnitus sufferers know how this disorder can be a real handicap, making it difficult to sleep, increasing the State ’ anxiety and stress.
When evaluating ORL is essential to assess whether l ’ Tinnitus can have an organic cause or less, Once satisfied that the tinnitus is idiopathic ’ (do not have a known cause) The patient must understand that tinnitus is a nuisance (also important) but it is not and must not represent a health problem. Continue reading
The plug of earwax
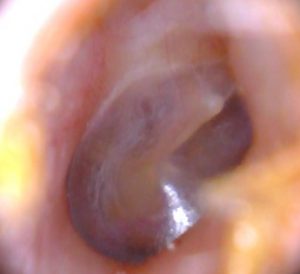
 L ’ outer ear physiologically produces ceruminose secretions that protect it from infection and microtrauma. Earwax is spontaneously spontaneously delivered from the skin to the outer ’ where will later be removed with normal hygiene. Earwax mingling to de-epithelialised skin can build up causing the dreaded Earwax plugs. Some people are very prone to the formation of earwax plugs, are known risk factors: l ’ hypersecretion of earwax, l ’ use of cotton buds (crushing Cerumen toward the eardrum), l ’ routine use of earphones, diseases that cause increased skin de ’ (keratitis, Psoriasis), narrow ear canal or shrink from osteomas and Exostosis. Also with age ear wax tends to be harder and so it is more prone to the formation of caps with ’ advancing years. Ear cerumen has a particular feature: is hygroscopic, namely swells when it's wet with water. And’ frequent that patients report feeling much less, suddenly, After taking a shower. Earwax plugs can give various symptoms: conductive hearing loss, autophony (hear their voices reverberate), Tinnitus, pain (ear pain) If they appear over infections. A simple otoscopy enables you to diagnose Cap. There are different techniques to remove plug of earwax. The simplest and the least disturbing to the patient is to resort to washing earphones: a jet of water ’ (at body temperature) sprayed in the external ear canal insinuates itself between the skin and Earwax him taking it off from. In the event that you suspect a ’ infection (already have pain) or there is a known perforation of tympanic basolateral or any other condition of ’ ears,or washing is however not recommended. You can remove the Earwax with hooks, Anse, spatulas, Hartmann's pliers or with suction under careful Visual inspection.
L ’ outer ear physiologically produces ceruminose secretions that protect it from infection and microtrauma. Earwax is spontaneously spontaneously delivered from the skin to the outer ’ where will later be removed with normal hygiene. Earwax mingling to de-epithelialised skin can build up causing the dreaded Earwax plugs. Some people are very prone to the formation of earwax plugs, are known risk factors: l ’ hypersecretion of earwax, l ’ use of cotton buds (crushing Cerumen toward the eardrum), l ’ routine use of earphones, diseases that cause increased skin de ’ (keratitis, Psoriasis), narrow ear canal or shrink from osteomas and Exostosis. Also with age ear wax tends to be harder and so it is more prone to the formation of caps with ’ advancing years. Ear cerumen has a particular feature: is hygroscopic, namely swells when it's wet with water. And’ frequent that patients report feeling much less, suddenly, After taking a shower. Earwax plugs can give various symptoms: conductive hearing loss, autophony (hear their voices reverberate), Tinnitus, pain (ear pain) If they appear over infections. A simple otoscopy enables you to diagnose Cap. There are different techniques to remove plug of earwax. The simplest and the least disturbing to the patient is to resort to washing earphones: a jet of water ’ (at body temperature) sprayed in the external ear canal insinuates itself between the skin and Earwax him taking it off from. In the event that you suspect a ’ infection (already have pain) or there is a known perforation of tympanic basolateral or any other condition of ’ ears,or washing is however not recommended. You can remove the Earwax with hooks, Anse, spatulas, Hartmann's pliers or with suction under careful Visual inspection.
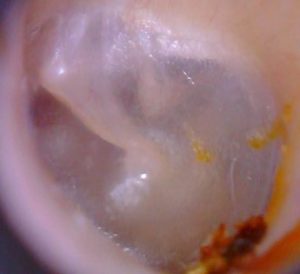
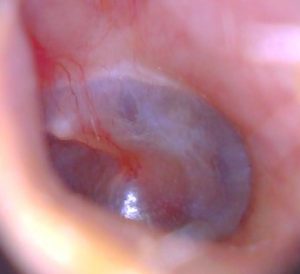
Otoscopy
L ’ Otoscope is an instrument with a graft for disposable ear cones, a light and a magnifying glass.
Allows you to observe the external ear canal and tympanic membrane in a much smoother. And’ simply effectual a slight pull towards the external ’ and later on the ear and place the instrument.
And’ possible to exclude the presence of earwax plugs, of narrowing of the external ear canal (Exostoses and osteomas), exclude external otitis, evaluate the tympanic membrane integrity ’, exclude miringiti, acute otitis media and effusive.
The exam can be done easily in children.
- « Previous
- 1
- 2
- 3









