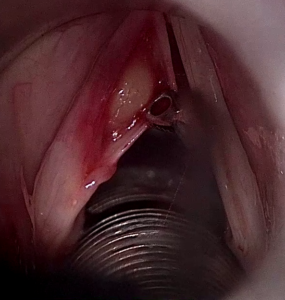
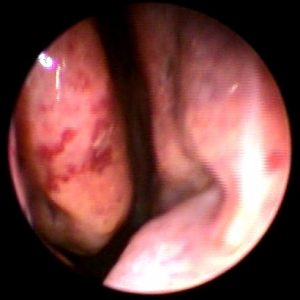
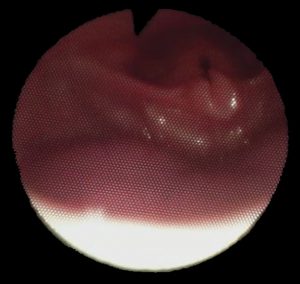
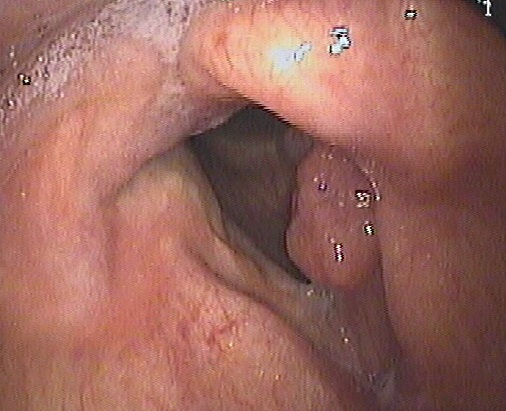
Nell’immagine si vede un particolare dell’intervento di asportazione di una cisti sottomucosa della corda vocale sinistra condizionante disfonia. La mucosa della corda vocale è stata incisa, scollata dalla sottostante cisti e ribaltata. L’intervento è stato effettuato in microlaringoscopia diretta in sospensione.