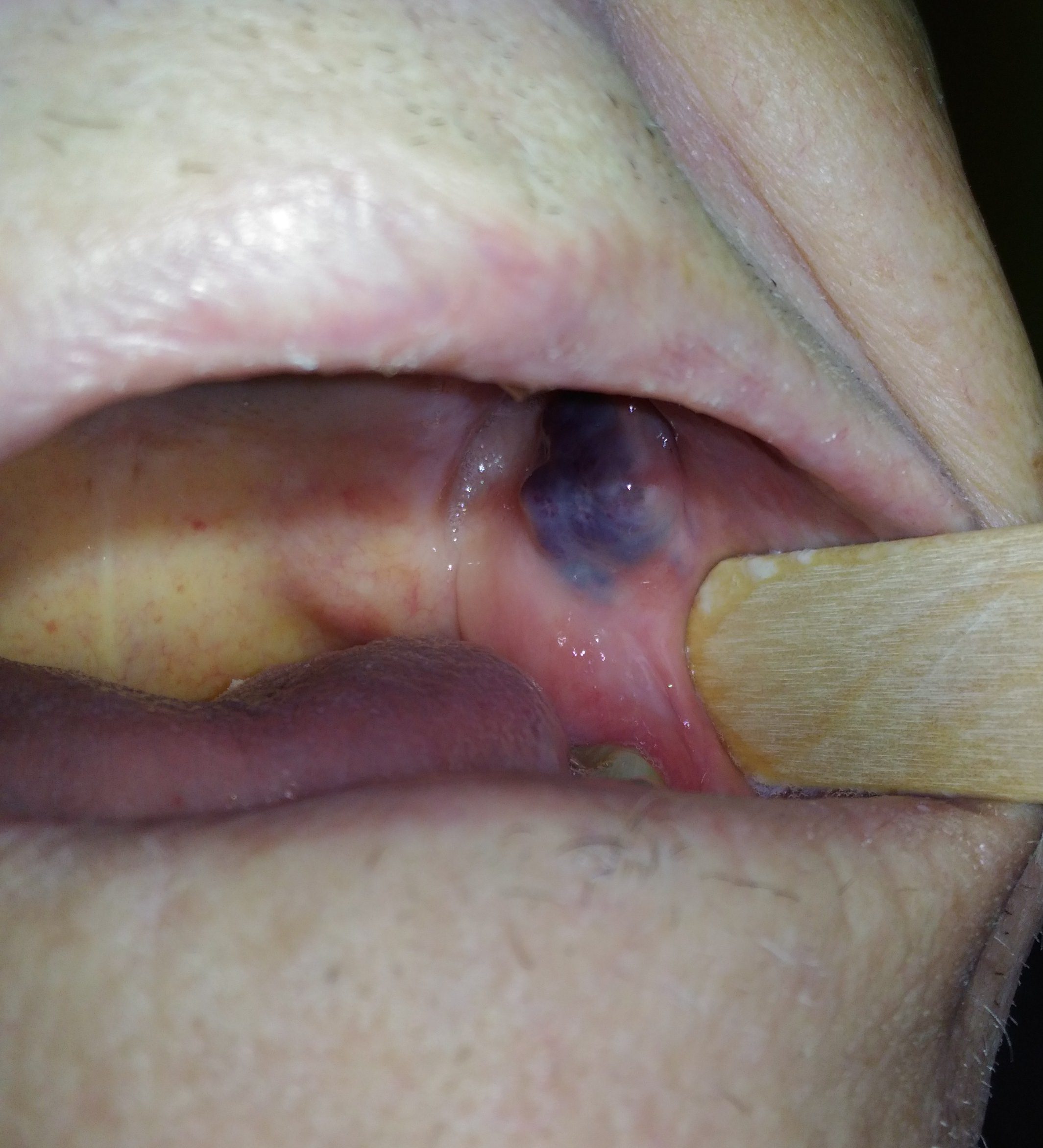
Oral Angioma


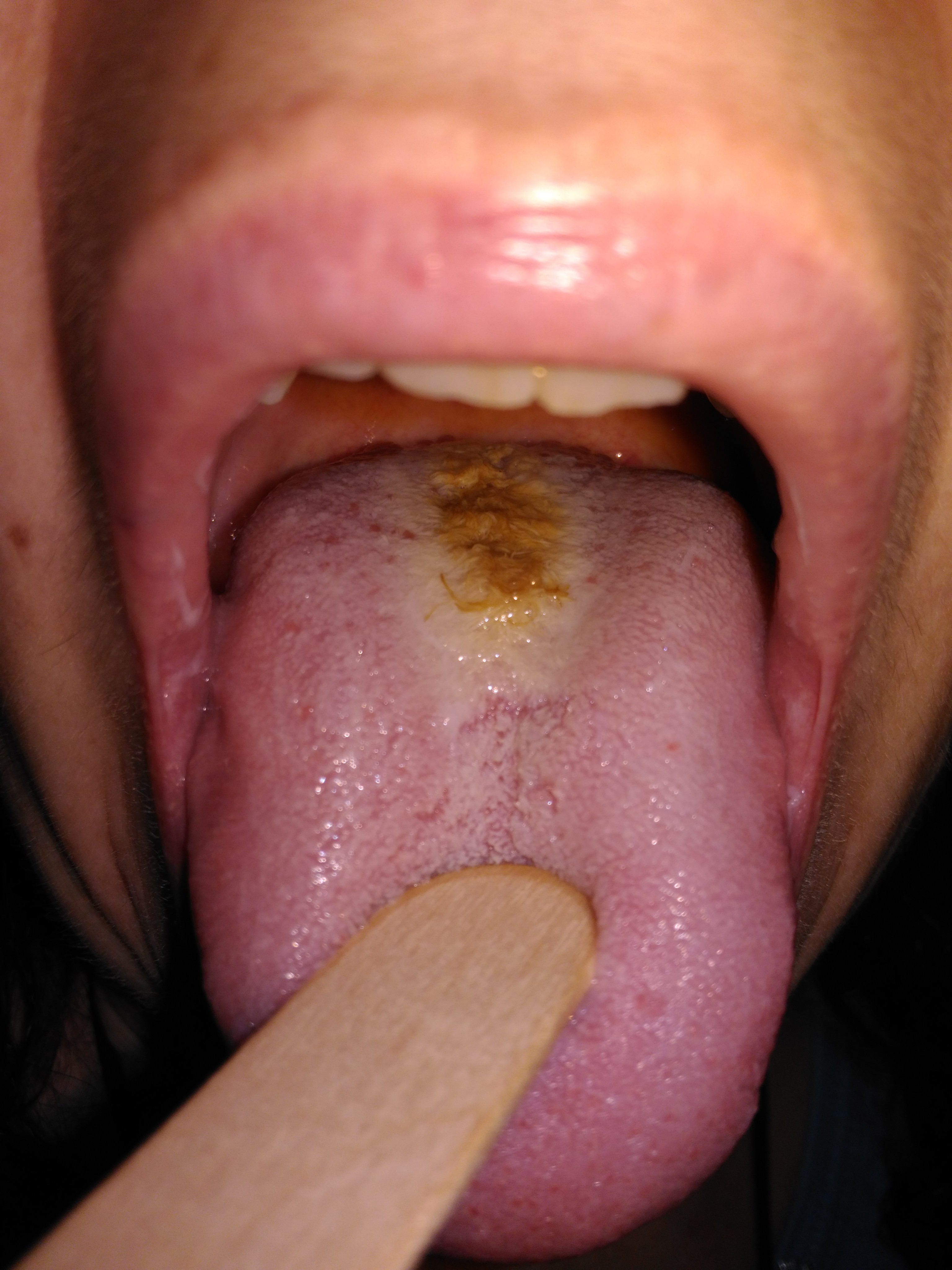
The language is an unusual condition where villosa nigra is a ’ important proliferation of microorganisms on the dorsum of the tongue. The colony, more frequently composed of bacteria, It's so large as to be visible to the naked eye as a dark spot, filamentosa.
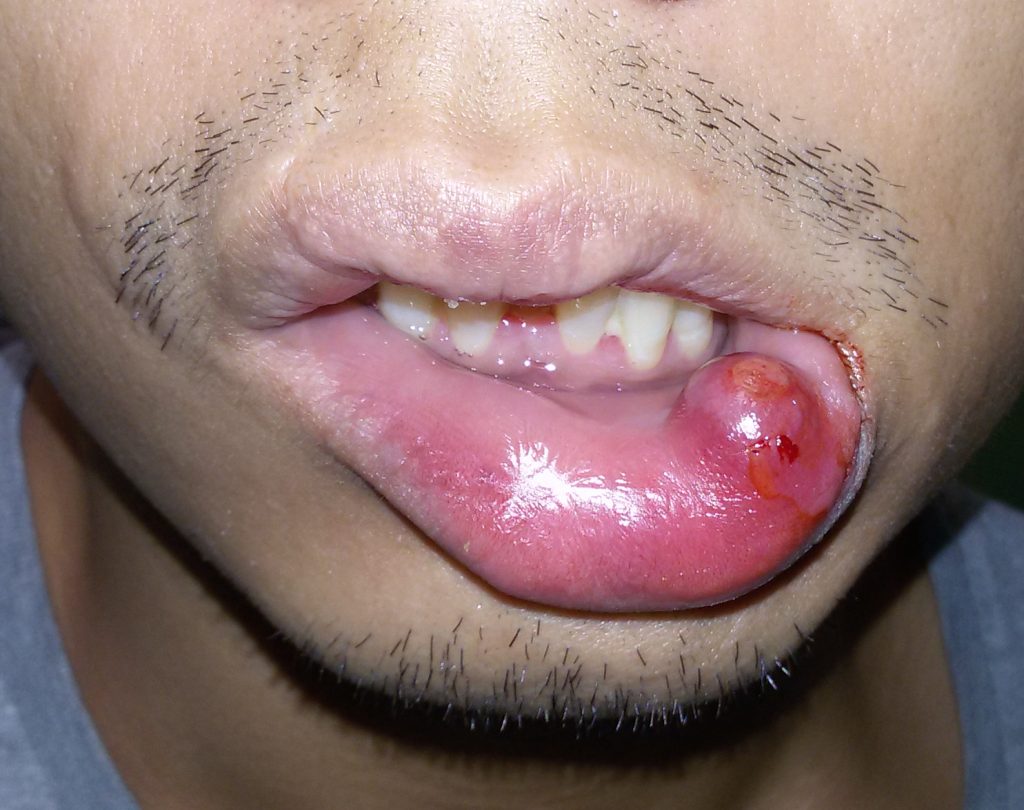
The minor salivary gland also referred to as retention cyst mucocele are due to ’ accumulation of saliva all ’ in a minor salivary gland duct occlusion of its, Typically after a trauma. Minor salivary glands are found on all the mucous membranes of the oral cavity (and with less density of ’ oropharynx), the more susceptible to trauma areas appear to mucoceles: the mucosa of the lips and cheeks. Continue reading →
Already several years ago surgeons ENT specialists realize that among patients with malignancies (typically with a ’ older than 60 years, smokers and drinkers) There was a small group of young patients and often non-smoking and non-drinkers.
Subsequent research has found and demonstrated the presence of tumors of all ’ within this second group of HPV virus (Human Papilloma Virus).
In recent years, however, was made a propaganda often alarmist and the wrong message that is often perceived by patients is that HPV causes cancer and that being a sexually transmitted viruses means that particular sexual habits cause cancer of the oropharynx.
The media starting with a kernel of truth have distorted reality by making several terrorism.
Continue reading →
L ’ intervention of tonsillectomy is a very simple procedure for the surgeon, routine, sure but it still sees a low complication rate.
The most feared complication is that you cannot reset hemorrhagic nohow. The bleeding risk remains regardless of any foresight or technology used in surgery.
The most critical days for bleeding are the first 2-3 days after ’ from the eleventh to the fourteenth ’ intervention and after the procedure. Continue reading →
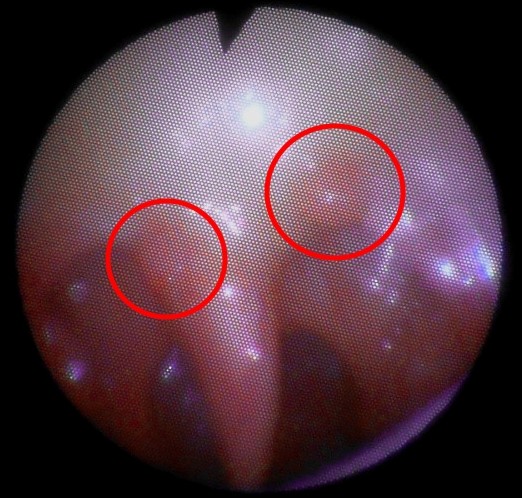
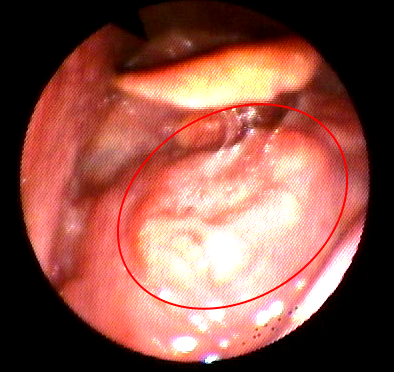
Oral papillomas are benign lesions and ’ from the ’ small oropharynx caused Human Papilloma Virus (HPV). Are generally caused by HPV types that are less likely to evolve to a malignant tumor. We recommend their removal as it can spread to healthy mucous to other parties. The transmission is solely from a human being all ’ other and predominantly through sex. In most cases, you can excise them by a simple operation under local anesthesia
For dysphagia means difficulty in swallowing solid foods and liquids
Main causes of dysphagia:
-Central neurogenic: stroke, brain injuries, dementia, Parkinson's disease, tumors of the brain stem, SLA, multiple sclerosis, Huntington's disease, poliomyelitis, syphilis.
-Peripheral neurogenic: peripheral neuropathy (Diabetes), myasthenia gravis.
-Muscles: polymyositis, Dermatomyositis, muscular dystrophy, Achalasia, diffuse esophageal spasm, LES hypertonia, Scleroderma
-Obstructive pulmonary disease: tumors, abscesses, Zenker diverticulum, Esophageal diverticula, extrinsic cervical masses, Mediastinal disorders, vascular disorders, cervical spondylosis, cicatricial esophageal rings, foreign bodies.
The Act-swallowing begins as a voluntary act and is subsequently brainstem coordinated from the nucleus of the solitary tract and nucleus ambiguous.
Swallowing the bolo meets a series of sphincters: sores, Linguo-Palatal, velofaringeo, the larynx, m. cricopharyngeus (RE4), LES. Continue reading →
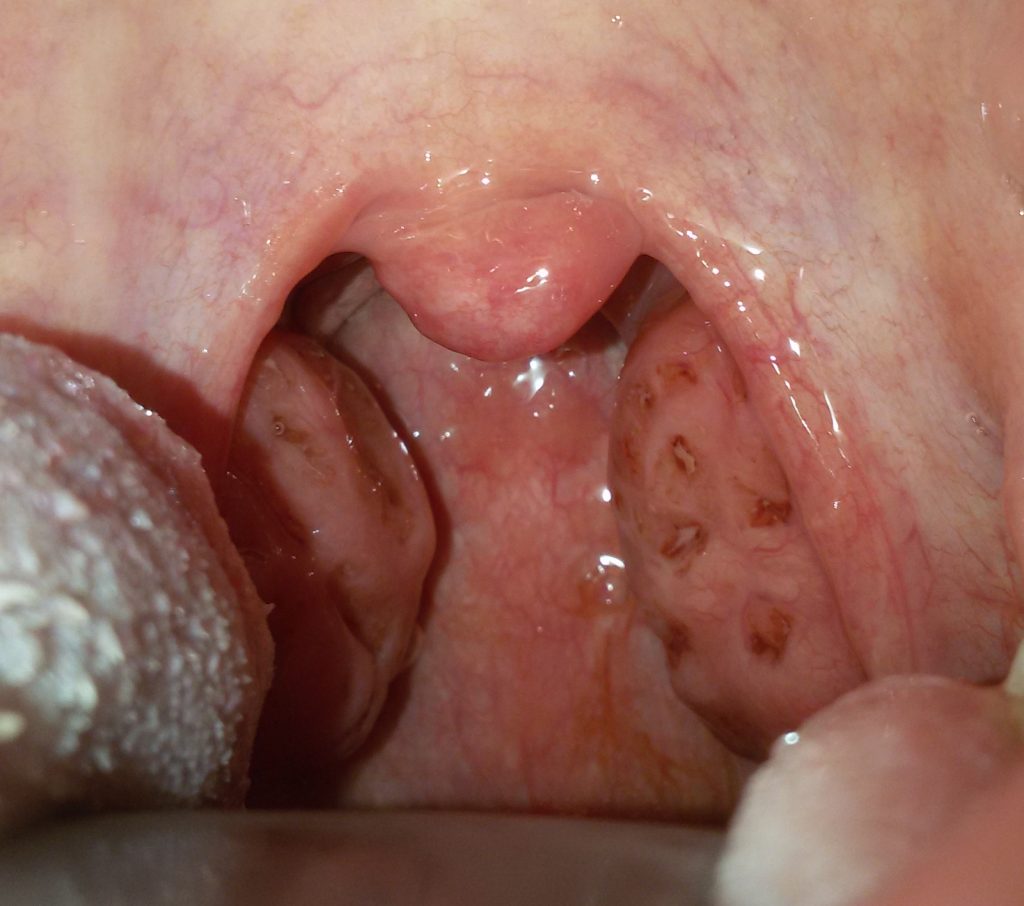
Tonsillectomy is surgery to remove ’ of the palatine tonsils. And’ a routine procedure, safe, that is currently being carried out under general anesthesia.
The tonsils are removed or infectious diseases (Recurrent acute tonsillitis) or for airway obstruction problems or suspected malignancy.
The criteria that lead to a correct indication for tonsillectomy differ substantially between children and adults.
Scientific Association for
training, of care and solidarity
in Otolaryngology