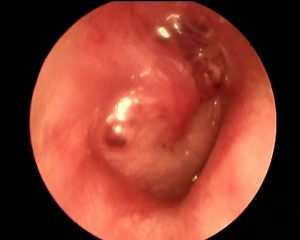
L ’ acute otitis media is the ’ infection, Typically, bacterial, Dell ’ middle ear. And’ characterized by a very intense pain, often button, that is accentuated by lying, It also causes hearing loss and feeling ovattamento headset, It is often accompanied by fever, headache and malaise. Can follow a ’ infection of the upper Airways or effusive otitis media ’.
And’ more frequent in children for a variety of anatomical and physiological reasons: the auditory tube are shorter, wider and more horizontal course by facilitating the passage of microorganisms from the nasopharynx all middle ear ’; children are unable to blow the nose properly, but they tend to suck the secretions; nasopharyngeal infections have more frequently for immaturity of the immune system; in the case of formula feeding are powered down instead of semi-sitting, making it harder to coordinate breathing and swallowing.
Other factors favouring l ’ otitis media are the winter season, low socioeconomic conditions, nursery, passive smoking, prematurity, allergies, immunocompetence, Brothers, prolonged use of pacifier during the day.
L ’ bacterial infection causes the formation of pus that accumulates in the middle ear ’ occupying all the space and preventing the transmission of sound, the production of pus continues exerting strong pressure on the tympanic membrane which results in severe pain. If the infection continues, the pressure can be sufficient to break the tympanic membrane and invade the external ear canal. When you create a perforation of the tympanic membrane relieves the pain and pus coming out of the ear canal (otorrhea).
Most of the perforations completely resolved after infection otitis close ’ l.
L ’ acute otitis media tend to heal spontaneously, and then can be corrected wait a few days before administering an antibiotic.
Diagnosis is based on medical history and medical examination with ’ otoscopy.
Rare complications are possible:
-infectious: acute mastoiditis, petrosite (can cause cavernous sinus thrombophlebitis), labyrinthitis, paralysis of n. Faciale, sigmoid sinus thrombophlebitis, extradural abscess, the brain, meningitis.
-for the non-completion of tympanic perforation: chronic otitis media simple.
-for scar effects/erosion for recurrent infections: miringosclerosi, tympanosclerosis, tympanic retraction pockets, atelectasis (medialization of the gable with reduction of the airspace of the middle ear).









