’ is the intervention of parotidectomy partial or total removal of the Parotid gland.
Parotid gland tumors is made especially to remove both benign and malignant. Only rarely do the problems of Parotid salivary calculi (scialolitiasi) require ’ ’ gland excision and the intervention of parotidectomy.
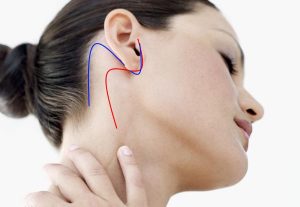
Engraving
There are several types of engraving which can be used for ’ intervention of parotidectomy.
L ’ most common incision is that according to Redon: you make a cut before all ’ ear starting from the root of ’ elice, go down until dell ’ ear lobe and then climb going back all ’ ear then turn back and go l ’ incision in the neck.
A variant is one that combines the previous incision with removal of wrinkles (facial lift): you make a cut before all ’ ear starting from the root of ’ elice, go down until dell ’ ear lobe and then climb going back all ’ ear, Unlike the previous incision, the denomination takes up all ’ the base of the scalp and then descends while remaining adjacent to the ’ base of the scalp, in this way the hair will cover l ’ incision.
Other variants do not perform l ’ incision in front of ’ ear.
Considerations on the ’ incision: generally we tend to make a large incision ’, a total of 7-9 cm, but this should not scare: have a better aesthetic result long incisions made taking into account the lines of force of the skin that do not will live short incisions which suture is. The portion of ’ incision in front of the ear ’ is the one that commonly heals better and tend to become invisible. The choice of ’ incision is made by the surgeon not only depending on the aesthetic result hoped for but also for technical reasons.
Technical notes of ’ intervention
Parotidectomy is usually performed under general anesthesia. To remove a tumor being l ’ removes a portion of the Parotid gland that contains within it the tumor. Parotid surgery is made complex by the fact that this gland is crossed by the facial nerve that allows muscle movement mimics on the side of the gland. The nerve has therefore an important role for the ’ aesthetics, non-verbal communication, for the protection of the ’ eye (a section of the nerve does not allow complete closure of eyelid) and for power ’ (a section of the nerve does not allow complete closure, “tight”, of the lips). Also the nerve splits all ’ inside of ghaindola in its branches and on the branches that have a calibre of less than one millimetre.
Before removing the gland with the cancer then proceeds to search for the facial nerve and all ’ isolation of its claws so as to remove the tumor while preserving the facial nerve and its branches.
In the event of malignant tumors surgery may be complex and may need to sacrifice some nerve branches and remove neck lymph node stations.
L ’ intervention lasts varies from 90 minutes at 3 hours depending on the type of tumor and its location. Is normally placed a drain that is kept for 3-4 days and removed before discharge.
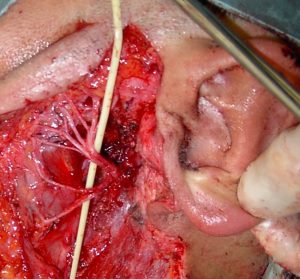
Complications of ’ surgery
Like all surgeries under general anesthesia, you may encounter problems with medications allergic-type anesthetics, There is a risk of bleeding and infection. In particular as regards the ’ intervention of low risk of injury parotidectomy partial or complete (rarisssime) facial nerve; also the residual portion of the Parotid gland can continue to produce saliva that not finding an outlet towards the mouth accumulates in the neck, performing periodic compressive dressings the problem tends to resolve spontaneously. Another rare complication of the parotidectomy Frey Syndrome: the nerve endings that went to the Parotid gland, After ’ surgery, they mistakenly to innervate the sweat glands of the skin, Here, therefore, that in a small proportion of patients we observe sweating cheek and neck skin especially during meals. This syndrome tend to resolve spontaneously in a good proportion of patients.









