 Pharyngeal tonsils or adenoids are lymphatic organ which is part of Waldeyer's ring and ’ are placed in the posterior wall of the nasopharyngeal cable, Anatomic area that connects the nasal cavity and oropharynx ’ where l drain the auditory tube tube. Given the small size of the bones of the child the nasopharyngeal cable has a greatly reduced volume than that of adult ’, also given the increased activity of lymphatic tissue in children volume adenoids is greater than that of adult ’. We understand how much easier it can occupy the adenoid tissue nasopharyngeal cable in the child. Adenoid tissue in children is physiologically hypertrophy but we speak of adenoid hypertrophy real when l ’ dimensions given lymphatic tissue causing problems.
Pharyngeal tonsils or adenoids are lymphatic organ which is part of Waldeyer's ring and ’ are placed in the posterior wall of the nasopharyngeal cable, Anatomic area that connects the nasal cavity and oropharynx ’ where l drain the auditory tube tube. Given the small size of the bones of the child the nasopharyngeal cable has a greatly reduced volume than that of adult ’, also given the increased activity of lymphatic tissue in children volume adenoids is greater than that of adult ’. We understand how much easier it can occupy the adenoid tissue nasopharyngeal cable in the child. Adenoid tissue in children is physiologically hypertrophy but we speak of adenoid hypertrophy real when l ’ dimensions given lymphatic tissue causing problems.
The symptoms may be caused by 2 different reasons:
1- auditory tube blocking the eustachian tube: the auditory tube enable mucus that normally forms all ’ ’ in the middle ear to drain out into the Gorge; If the adenoids blocking the eustachian, Nell ’ affected ear will accumulate mucus that will prevent the transmission of sound causing a ’ hearing loss; also the mucus that stagnates promotes the development of bacterial colonies and then the appearance of recurrent acute ear infections. The issue may affect one and both ears
2- obstruction of nasal breathing: the child who is not breathing properly from your nose will compensate by breathing chronically from the mouth and face and facial bones adapt their shape to streamline mouth breathing: you will develop a palate with a pointed shape (an arc), Dental occlusion problems, the protruding upper lip. The biggest problems you will have however at night: the child will try to breathe better assuming a position often supine position with the head hyperextended, difficulty breathing during sleep will cause snoring, a rough and poor. Children with adenoid hypertrophy tend more easily than others to bedwetting. If a child sleeps badly, during the day you may be drowsy more frequently or hyperactive, rough, irritable, easily distractible. These problems associated with ’ hearing loss may justify a significant slowdown of ’ learning. Not passing properly l ’ air from the nasal pits, the mucus tends to stagnate and you have frequent infections of the upper airway (particularly rhinitis and adenoiditis). Often but not always l ’ adenoid hypertrophy is associated all ’ tonsillar hypertrophy.
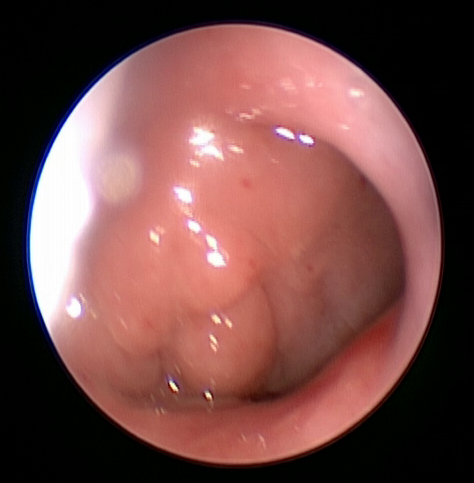
To diagnose l ’ adenoid hypertrophy is often enough to talk with parents, evaluate symptoms and observe how the child breathes. To quantify l ’ l ’ therapeutic hypertrophy and decide you need to make a fiberoptic (When the child has at least 2-3 years) or alternatively perform an x-ray latero-lateral.
You can counteract l ’ adenoid hypertrophy is medically, based on nasal washes and steroid medication through spray or via the ’ intervention of adenoidectomy. L ’ is very quick intervention adenoidectomy, performed under general anesthesia, lasting a few minutes, pretty sure, characterized by a very low complication rate that solves rapidly your problem. Often already after 2 weeks parents report that the baby resting well, Russian not more and is more attentive and quiet









