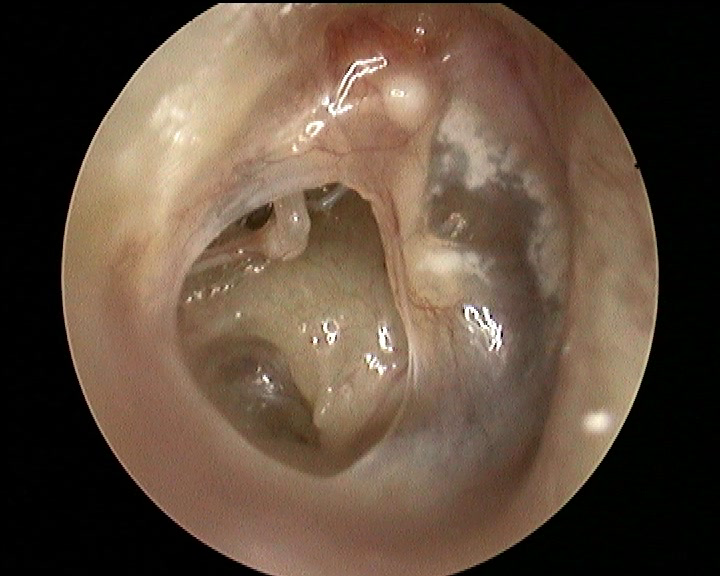
The tympanic membrane has an elliptical shape and completely isolates the middle ear from the outer ear canal.
Has a dual function:
-barrier, protecting l ’ middle ear infections
-amplify sounds and pass them on to the auditory ossicles.
And’ consisting of three layers: skin on the external side, connective tissue and mucous layer on the internal side.
The membrane can go in against such a perforation or infection or a trauma ’.
In the event of a’acute otitis media, the pus that accumulates in the ’ middle ear can exert pressure on the membrane to tear the cloth. When this happens the patient notices a sudden decrease ’ pain and discharge of pus from the ear ’ (otorrhea).
Trauma can be managed (cotton buds, foreign bodies, cleaning operations) or indirect damages, to increase pressure (barotraumas, diving, open hand slap on ’ ear).
The perforations of the tympanic membrane can
go against spontaneous healing or become chronic.
In children can occur very frequently after ear infections and tend to resolve spontaneously in most cases.
When a perforation does not closes we speak of simple otitis media: the patient may complain of hearing loss (even very slight in the case of minor perforations), also the drilling can be a gateway for bacteria and then you will have frequent ear infections, characterised by cerebrospinal fluid but not violent grief (barring complications).
In the long run skin cells can migrate from the pipe in ’ middle ear and form a cholesteatoma that tends to rise eroding the facilities of ’ middle ear and/or adjacent structures.
If you notice a tympanic perforation is appropriate to make an assessment audiologica that may indicate the presence of cholesteatoma or erosions of auditory ossicles.
L ’ otoscopy and l ’ endoscopy can evaluate the health of ’ middle ear by identifying or excluding a cholesteatoma. In cases of doubt, it may be useful to establish TC and/or MRI.
And’ always recommended surgical resolution of drilling (myringoplasty) It is usually performed under general anesthesia, both to improve l ’ heard that to isolate from the middle ear ’ external ’ again. In the event that for the ’ age or comorbidity you choose not to l ’ intervention are important periodical checks









