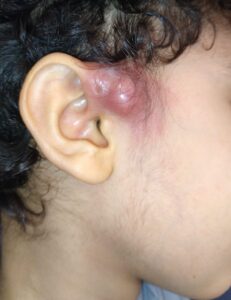
Bambino affetto da cisti preauricolare (primo arco branchiale) infetta. Posteriormente alla cisti, davanti alla radice dell’elice, è possibile osservare lo sbocco del tramite fistoloso.

Bambino affetto da cisti preauricolare (primo arco branchiale) infetta. Posteriormente alla cisti, davanti alla radice dell’elice, è possibile osservare lo sbocco del tramite fistoloso.
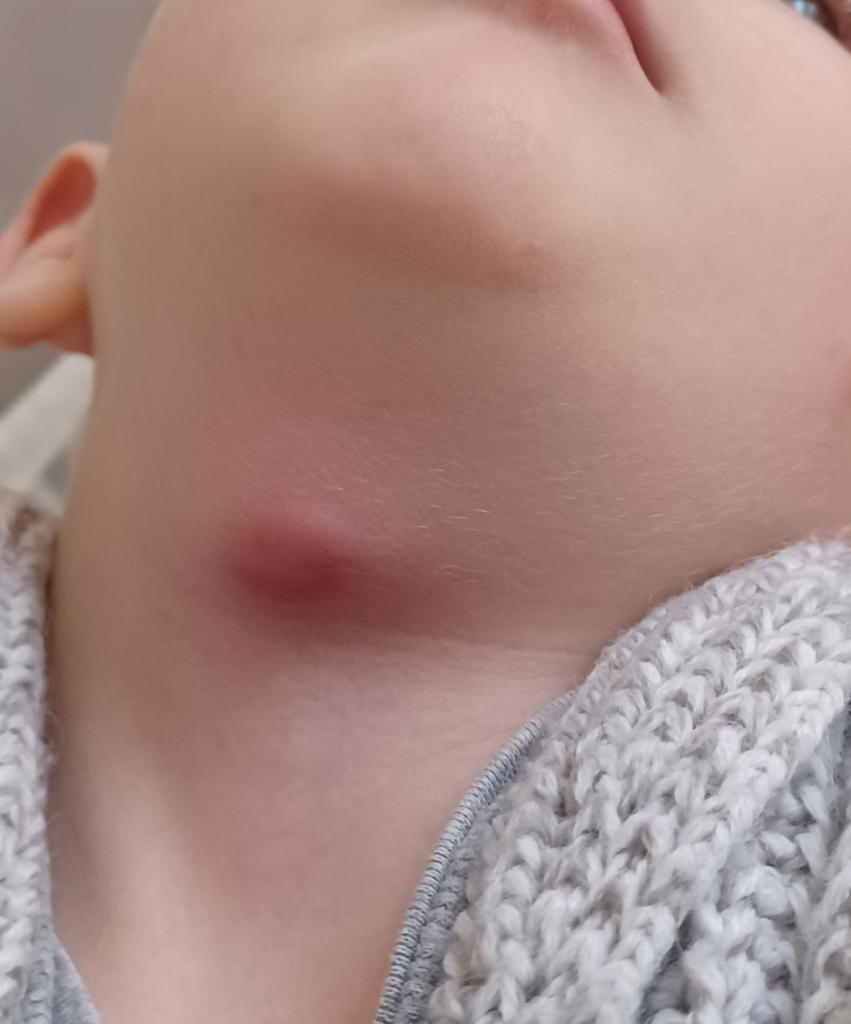
Cisti del dotto tireoglosso infetta di un bambino di 2 years. Nella maggior parte dei casi, la cisti del dotto tireoglosso si presenta come una massa teso-elastica, indolente, mediana del collo. Può andare incontro a sovrainfezione e raramente può essere sede di tumori di origine tiroidea.
In genere la cisti del dotto tireoglosso viene studiata con ecografia, risonanza magnetica e spesso anche con agoaspirato. La diagnosi é meno frequente in età pediatrica.
Il caso della foto é di un bambino di 2 anni la cui diagnosi é stata fatta dopo accesso in PS per sovrainfezione della cisti. Inizialmente era stato concordato di procrastinare l’intervento fino ai 3-4 anni ma il bambino ha avuto plurimi episodi di infezione nonostante drenaggio del pus ed adeguata terapia antibiotica.
É stato quindi effettuato l’intervento all’età di due anni e mezzo asportando, come da tecnica, oltre alla cisti anche il residuo del dotto e il segmento centrale dell’osso ioide con risoluzione della problematica.
Il Coblator genera un flusso di plasma sulla sua punta che è in grado di vaporizzare i tessuti senza generare una quota significativa di calore, è così possibile asportare un tessuto senza danneggiare quelli adiacenti.
Questa tecnica viene sfruttata in modo molto vantaggioso nell’intervento di tonsillectomia con un approccio leggermente differente dalla tecnica tradizionale. The classic tonsillectomy He plans to remove the entire tonsil, including both his parenchyma and his fibrous capsule that houses it. When using the plasma scalpel (Coblator ®) A slightly different technique is performed, la tonsillectomia intracapsulare con coblation, removing the tonsil parenchyma but leaving the fibrous capsule of the tonsil in place.
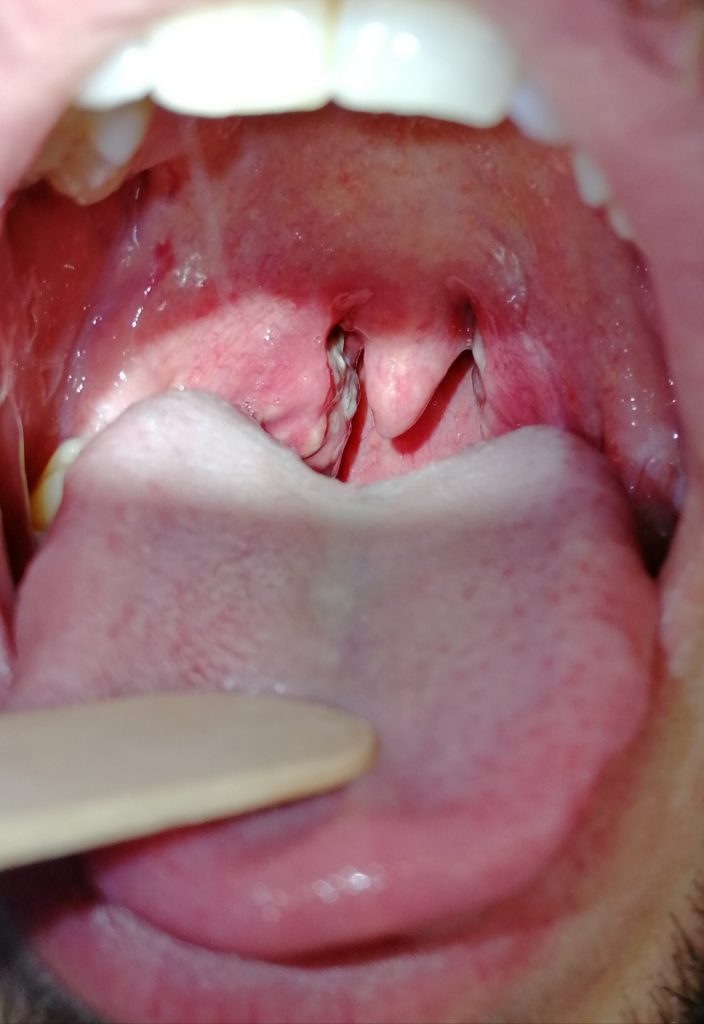
For acute tonsillitis means inflammation of the pharyngeal tonsils, often associated with inflammation of the tonsils and adenoids retrolinguali in a context of pharyngitis.
In the first years of life are mainly viral while from 5-6 years are predominantly bacterial. Continue reading →
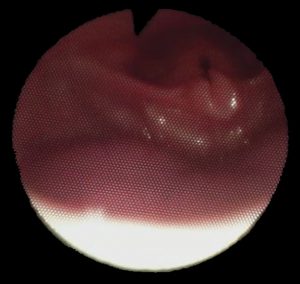
The laryngomalacia is a congenital disorder characterized by flaccidity of laryngeal cartilages and in particular of the epiglottis that tends to “curl up” and to replicate themselves inside during inspiration. This phenomenon causes an inspiratory stridor also very strong which tends to alarm the parents. Occasionally the laryngomalacia is able to clog the Airways causing a real shortness of breath.
Despite being a congenital stridor problem generally begins after 4-6 weeks, worst progressively up to 6-8 months and tend to resolve spontaneously after the 2 years.
Only rarely is necessary a surgical procedure.
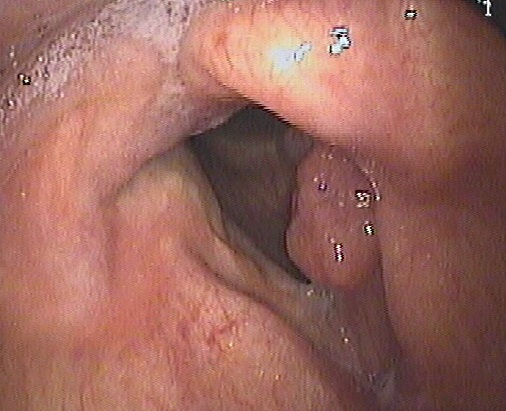
The laryngeal Papillomatosis is a disease caused by viruses belonging to the family of Papovaviridae (HPV) mainly 6 and 11 which is characterized by the appearance of papillary lesions laryngeal mucosa morphology exophytic lesions, characterized by high rate of recurrence after treatment.
The main location of the disease is laryngeal level, the lesions are seen less frequently throughout the aero-digestive tract.
The disease is characterized by recurrent clinical course, time-varying, ranging from spontaneous resolutions up to multiple relapses over periods of wellness 20 years.
And’ a benign disease, However, associated with high morbidity for possible wide diffusion the Airways, for the recurrent and trend for malignant transformation even though infrequent. Continue reading →
Nasal Endoscopy is a non-invasive outpatient procedure of exploration of the nasal cavity by means of a rigid endoscope or fiberscope. The procedure is generally well tolerated and causes a slight annoyance. Sometimes you may need to use local anesthetic and/or decongestant to reduce swelling of the mucous membranes and make more accessible the exploration of the nasal cavities. Continue reading →
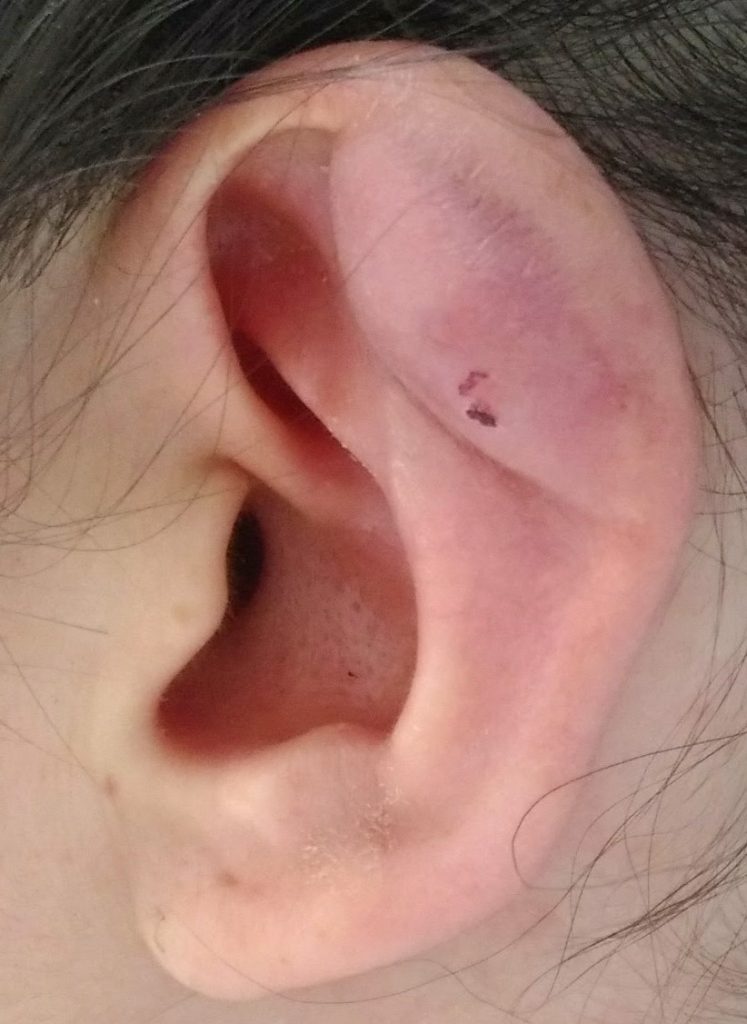
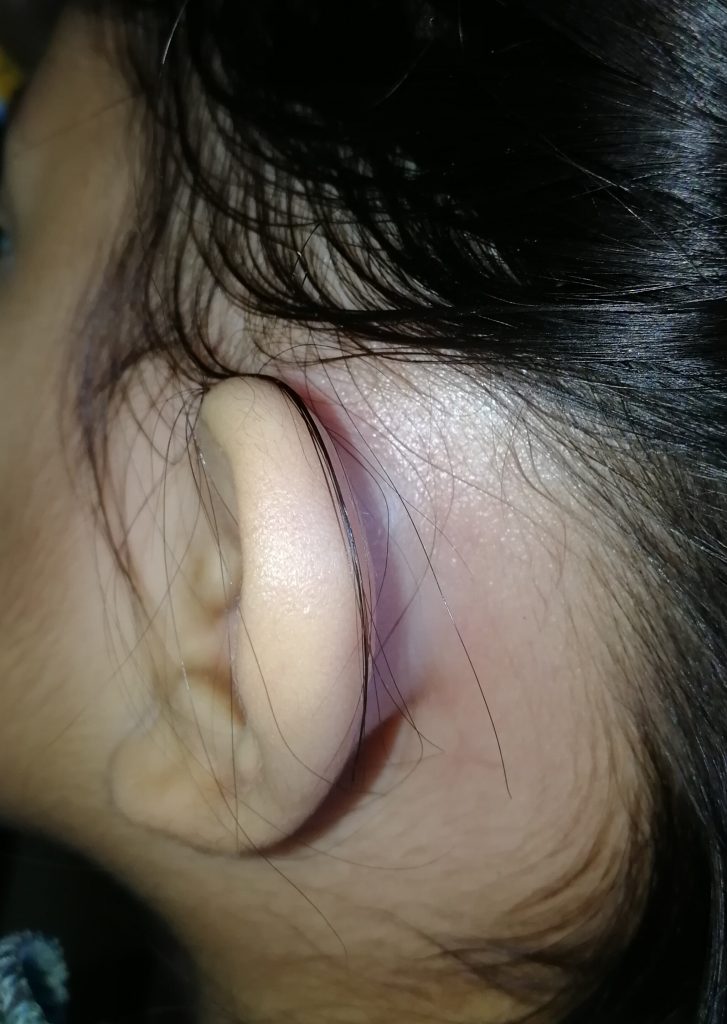
Trauma and foreign bodies can cause infections of the ear, If the pus can't escape outside can accumulate in the Hall, creating a swelling.
Sometimes an ear trauma can cause bleeding that accumulates in the Hall by creating a otoematoma, a swelling that look very similar to an abscess but in the absence of infectious processes.
Accidental ingestion of foreign objects is a frequent cause of evaluation at the emergency room. Foreign bodies can be foodborne (fish bones or bone) or toys (typical of children) or other materials (especially in psychiatric patients) and can penetrate mucous membranes aereodigestive tract and then have an evaluation by the Otolaryngologist. Continue reading →
Scientific Association for
training, of care and solidarity
in Otolaryngology