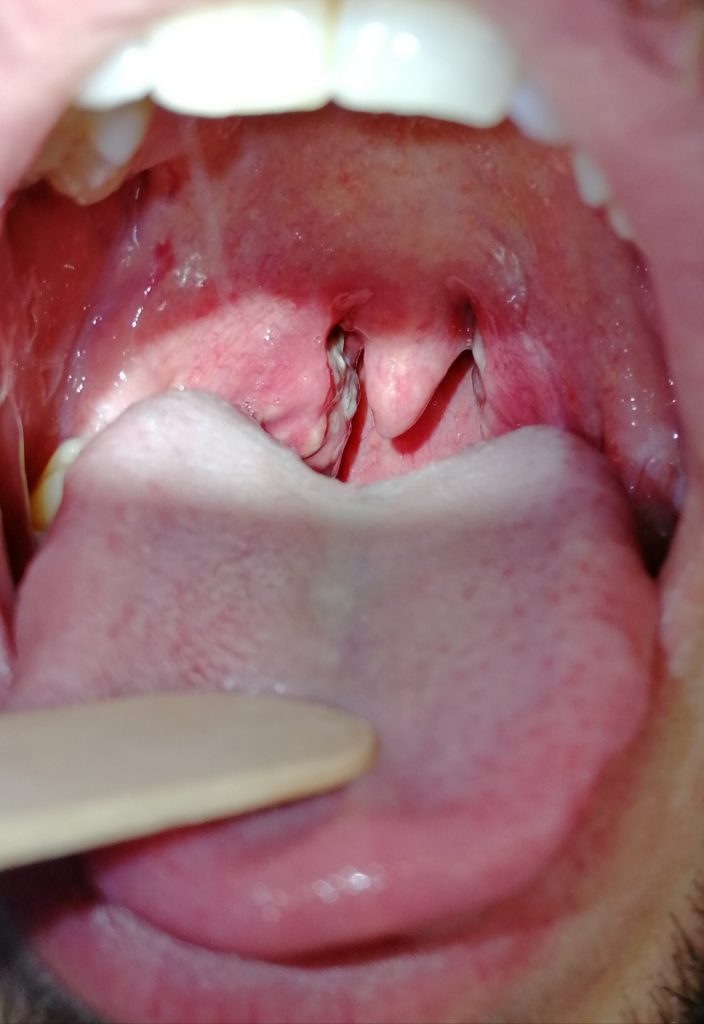
For acute tonsillitis means inflammation of the pharyngeal tonsils, often associated with inflammation of the tonsils and adenoids retrolinguali in a context of pharyngitis.
In the first years of life are mainly viral while from 5-6 years are predominantly bacterial.The acute tonsillitis occurs with faringodinia (pain in the throat), swallowing difficulties (Dysphagia), painful swallowing (odynophagia), otalgia reflected, fever, malaise, asthenia (fatigue), appearance of laterocervical adenopathies often painful.
The volume tonsillitis may be such as to hinder respiration requiring the mouth breathing and causing snoring.
Objectively there is a clear increase in the volume of tonsils (hypertrophy) appearing skin and covered with whitish secretions, dense. Pharyngeal mucosal hyperemia is also observed and enlargement of lymph nodes in the neck.
Without treatment the symptoms may persist for one to two weeks and can lead to complications.
The most feared complication is the peritonsillar abscess in which the pus accumulates in the spaces on the side of the tonsil, highlighting the pain and causing inflammation of the masticatory muscles resulting in trismus (inability to open the mouth).
While tonsillitis ancuta is generally treated at home, the peritonsillar abscess requires hospital admission for execution of drainage collection and intravenous therapy.
Both in the case of tonsillitis that abscess formation is important to ensure adequate hydration.









