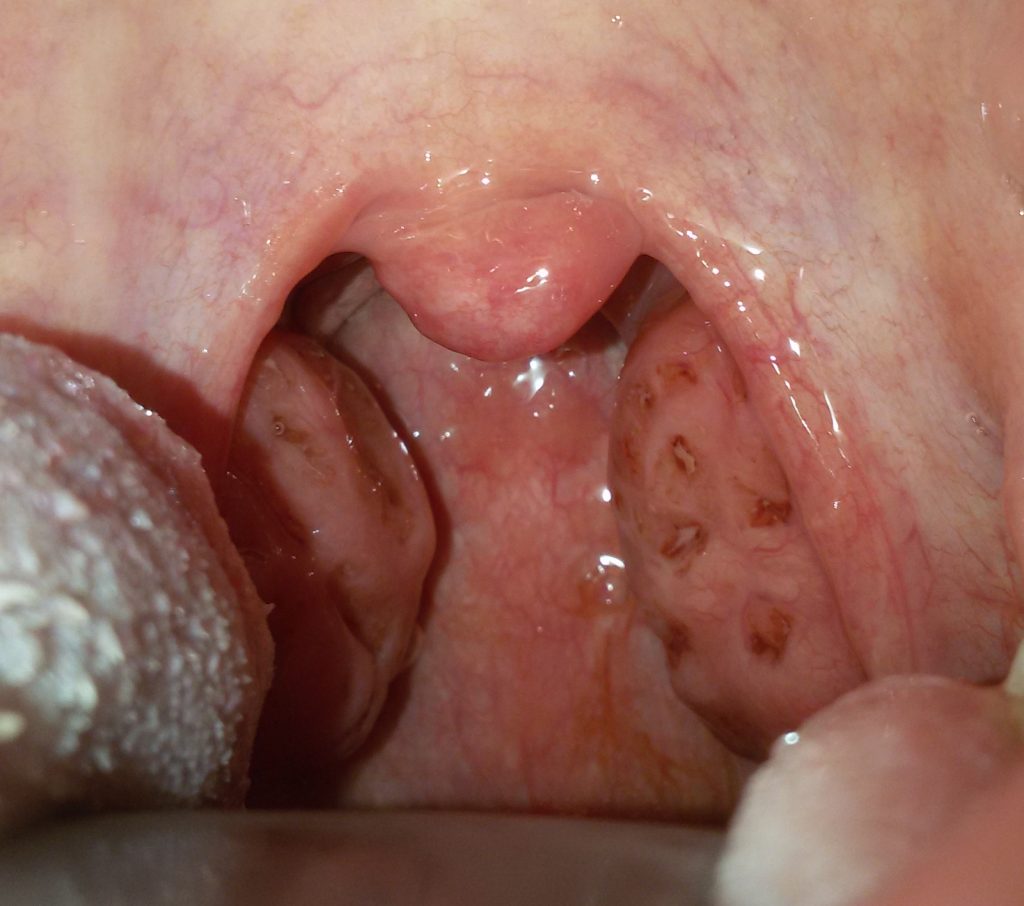
Tonsillectomy is surgery to remove ’ of the palatine tonsils. And’ a routine procedure, safe, that is currently being carried out under general anesthesia.
The tonsils are removed or infectious diseases (Recurrent acute tonsillitis) or for airway obstruction problems or suspected malignancy.
The criteria that lead to a correct indication for tonsillectomy differ substantially between children and adults.
In fact, tonsils are part of the lymphatic tissue of Waldeyer's ring ’ that it is important to protect the Airways against infection especially in the first years of life, at this stage children see for the first time new microbes (bacteria, mushrooms, virus), the immune system develops and matures it is therefore normal that children are subjects more than adults to infection; being also the lymphatic system in fervent activity is common to get a feeling for hypertrophic tonsil, diffuse laterocervical lymph node hypertrophy and adenoid hypertrophy.
With the ’ age, the immune system becomes more efficient and the lymphatic tissue of Waldeyer's ring ’ (palatine tonsils, pharyngeal or adenoids and lingual) tends to regress even almost completely.
From these premises, we understand how important it is to try to preserve the tonsils especially in children early in life and then you will have to wait until the child suffers from a rather high number of acute tonsillitis before recommending l ’ intervention. Nell ’ adult instead considering also pathologically acute bacterial tonsillitis are shrinking over time.
Another important indication all ’ intervention of tonsillectomy in children is often due to respiratory obstruction ’ ’ ’ tonsillar hypertrophy associated with adenoid hypertrophy. If the tonsil volume is likely to obstruct the passage of pharyngeal air ’ your baby rests badly and sleep apnea may occur resulting in reduction of ’ blood oxygenation. A child who rests badly is less attentive during the day, often hyperactive, irritable, view dell ’ learning and psychomotor development delay. Also the lack of oxygenation of the blood at night may influence the development of cardiovascular disease.
So when you have a diagnosis of sleep apnoea syndrome related to tonsillar hypertrophy is important subject the child to intervention of tonsillectomy to allow proper growth.
In adults is much more difficult than the single tonsillar hypertrophy is responsible for sleep apnoea syndrome (OSAS); most commonly OSAS ’ ’ dell l adult is multifactorial and therefore could be recommended to remove the tonsils in combination with other medical or surgical measures.
Other indications are all ’ metafocali syndromes tonsillectomy surgery (rheumatic fever, post streptococcal Glomerulonephritis, Sydenham Chorea ADHD (Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder), PANDAS syndrome (Pediatric Autoimmume Psychiatric Disorder Associated with Streptococcical infection), Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome), PFAPA syndrome (Periodic Fever, Aphtosous stomatitis, Pharyngitis and cervical Adenitis), previous peritonsillar abscesses, dyslalia, Dysphagia, suspicion of malignancy.
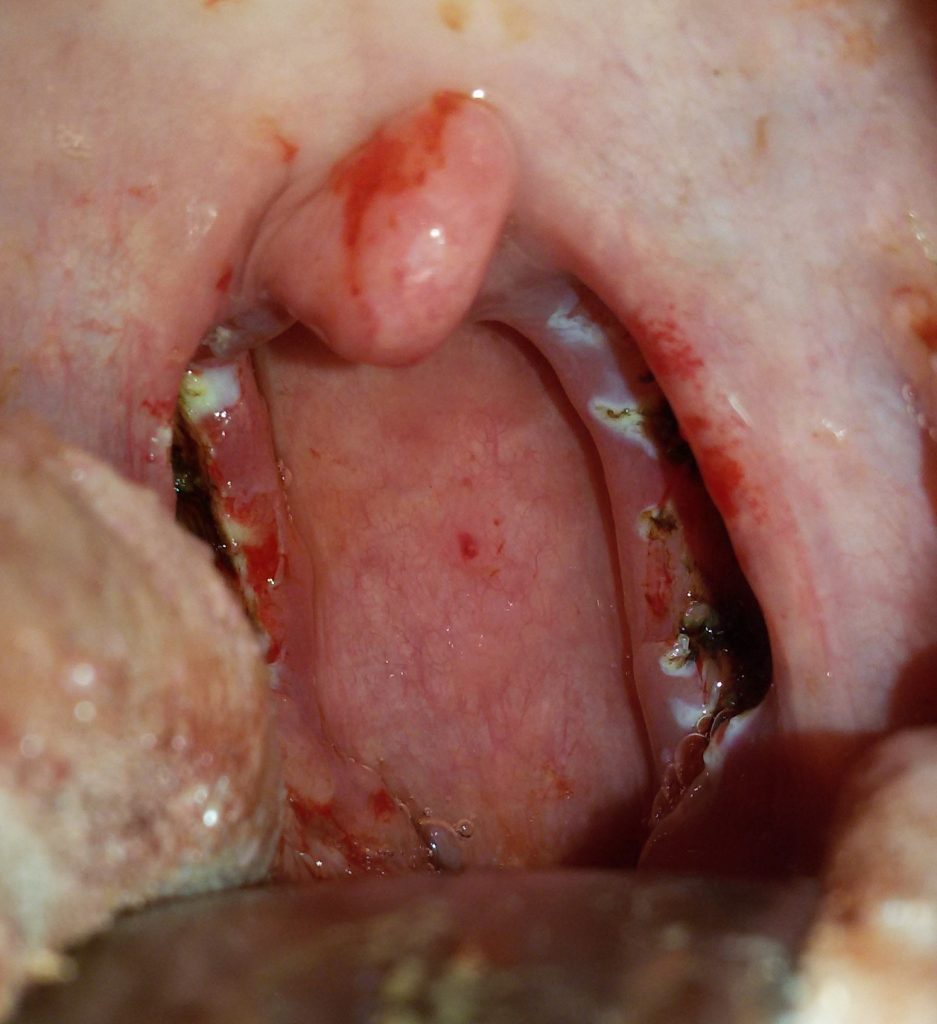
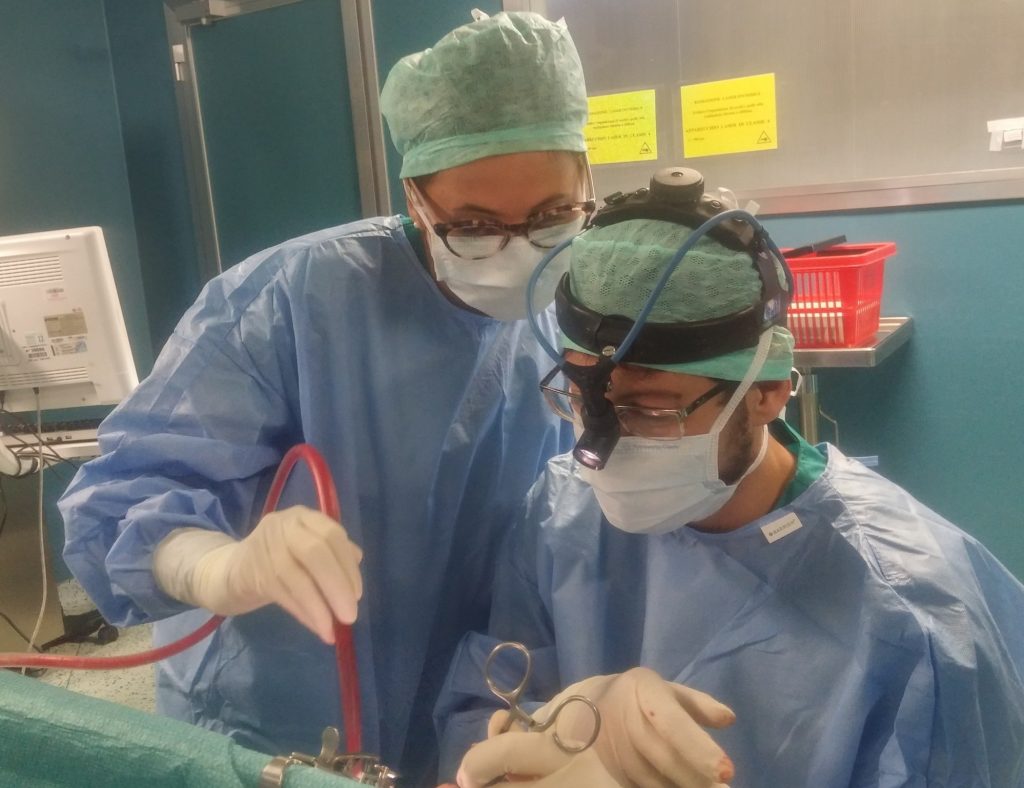
L ’ surgery is performed under general anesthesia and can be associated or not all ’ adneoidectomia surgery. The patient is positioned supine and tonsils are removed through the mouth, the surgeon is positioned generally at the patient's head. L ’ intervention is fairly smooth and lasts about 30 minutes. The tonsils are removed in most cases with traditional instruments (scalpels and scissors) and l are used to block bleeding electrocoagulation device for ’ (bipolar forceps) Hemostatic wire.
The most innovative tools have been proven as the ultrasonic scalpel, il laser e l’elettrobisturi ma nessuno di questi ha dimostrato un significativo e rilevante miglioramento dei risultati. Solo recentemente, la tonsillectomia con plasma, ha dimostrato una riduzione dei tempi di recupero e una riduzione del rischio emorragico.
No technology and no surgical shrewdness has managed to clear the complication rate. The most important complication is bleeding that although rare is not entirely negligible. Bleeding may occur either immediately after ’ surgery or after a few days. The most critical period it has 12-14 days after ’ surgery when disconnecting l ’ eschar, the scar covering the tonsils.
To minimize the risk of bleeding is important:
-soft diet and not hot to 2-3 weeks
-avoid physical exertion or exercise for 3 weeks
-’ avoid direct sunlight or heat sources
-do not take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (FANS, as acetylsalicylic acid, ibuprofen, nimesulide …)
Are generally recommended 1-2 controls in the postoperative period to verify the degree of scarring and to give the green light for the resumption of normal life and diet.









