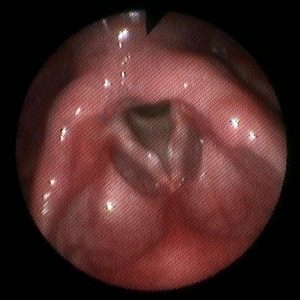
Vocal cord nodules are benign lesions that form for an incorrect use of voice or vocal abuse, both in adults and in children.
Incorrect use of the item may cause chronic microtrauma of the vocal cords which react by creating a thickening to try and protect yourself. Such thickening (the nodules) don't allow a correct closure of the vocal cords during phonation and cause then an entry “dirty” (dysphonia).
It triggers a vicious circle whereby the patient trying to get a better entry further dimension by getting a larynx aggravation endeavors of nodules.

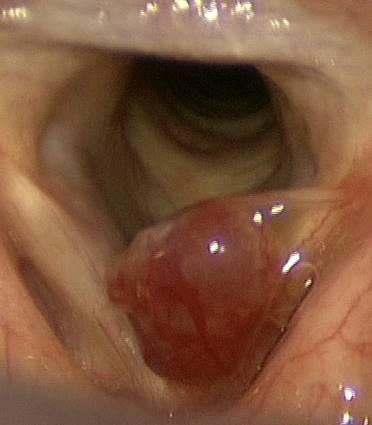
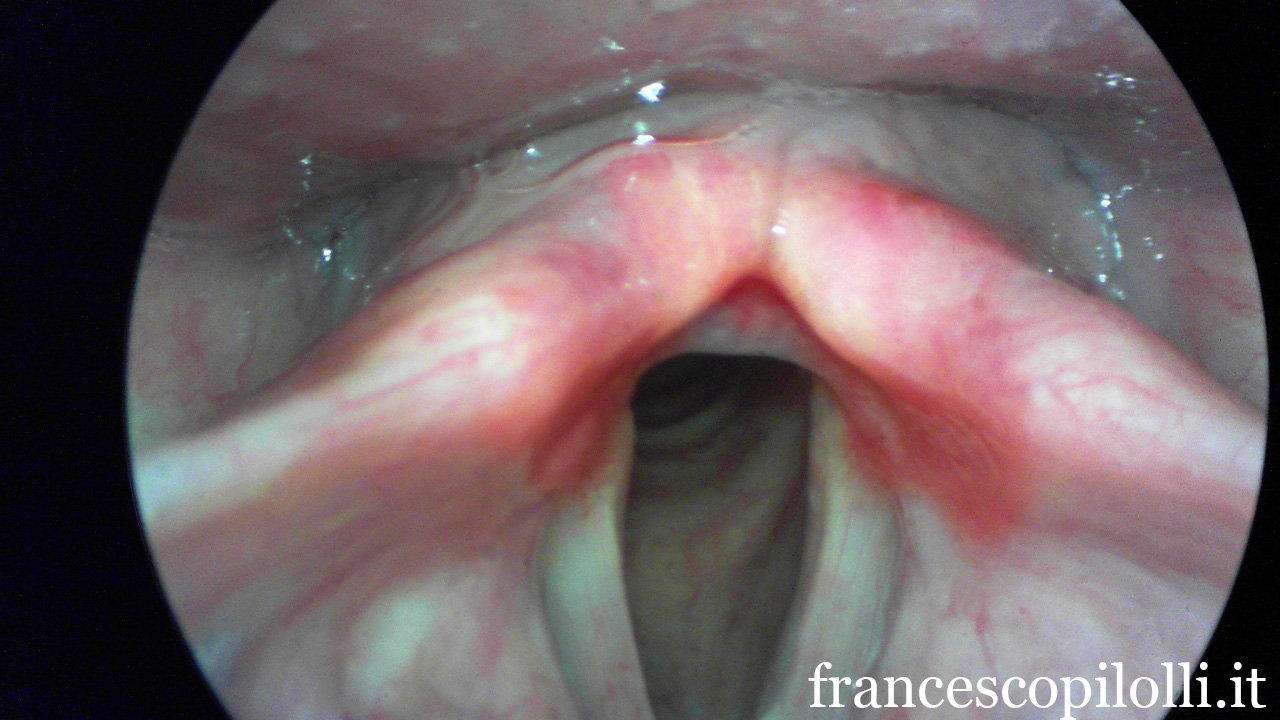 Symptoms may indicate this problem, to clarify the diagnosis and to rule out more serious especially morbid situations it is important to
Symptoms may indicate this problem, to clarify the diagnosis and to rule out more serious especially morbid situations it is important to