Thyroidectomy is removal of the thyroid gland surgery ’.
It is necessary in the event of:
-malignant tumor suspicion or ascertained
-goiter (or struma) whose volume is important and goes to cause cosmetic problems or deviation of the trachea or dyspnoea or dysphagia
-hyperthyroidism is no longer controllable with medical therapy
-graves ' disease with ophthalmopathy Continue reading
Neck, hypopharynx, larynx, thyroid and salivary glands - 3. page
Speaking after total laryngectomy
LASER surgery of the larynx, the laringectomie subtotals and improved radiotherapy allow many patients to treat cancers of the larynx without excise it completely.
Unfortunately still today many cancers of the larynx and pharynx can be carried out only with the intervention of ’ total laryngectomy (eventually extended to the pharynx: faringolaringectomia)
L ’ l ’ total laryngectomy speech expected removal of the entire larynx, l ’ interview of the trachea to the skin (full permanent tracheostomy) and the rebuilding of a new food away completely independent of the airway. At discharge, patients undergoing total laryngectomy eat normally through the mouth but breathe exclusively through the Trach (no longer from the mouth and nose).
Patients often see this intervention as very mutilating but actually you can live with it almost normally: tracheotomy can be easily hidden by a scarf or clothing with the neck slightly’ tall and you can retrieve your voice! Continue reading
Vocal cord paralysis
The 2 vocal chords are the structures that make it possible to produce sound by modulating the voice.
The vocal cords can stop moving or partially (paresis) or completely (paralysis). Their lack of mobility may be due either to a mass that blocks (carcinomas) or block of arytenoid articulation between the ’ ’ and the cricoid cartilage (rare, for arthritic phenomena, traumatic or necrosis of cartilage) or, most frequent situation, for a non-nervous control of the vocal cords (ricorrenziale palsy).
Nerve pathways may be broken or the central nervous system or peripheral level. Your vocal chords are controlled by the inferior laryngeal nerves (or recurrent nerves) that detach from the tenth cranial nerve (vagus nerve) in the cervical, descend down to chest level (right subclavian artery and left surround ’ surround l l ’ aortic arch) and then go back into the neck (Why are also called recurrent nerves) going to innervate the larynx. Rarely, to the right, the inferior laryngeal nerve can go to innervate the larynx directly without descending into the thorax (recurrent nerve not applicable).
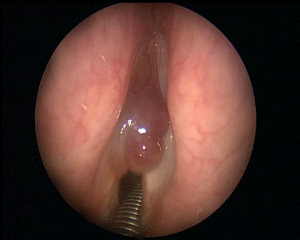
The precancerous and malignant tumors of the vocal cords
Even the mucous membranes of the larynx and in particular of the vocal cords can degenerate form of malignant tumors (predominantly squamous cell carcinomas).
This phenomenon occurs mostly in patients who smoke or who drink alcohol are chronically.
The degenerative process is a long process, characterized by several stages that are collected in the generic definition of Squamous intraepithelial lesions (Sils). Some types of SILs are self-limiting and reversible, Some are stable, other proceeding inexorably towards the SCC, Despite an adequate follow-up and treatment.
The most frequently used classification is the one offered by the World Health Organization (Who) in 2005, distinguishing laryngeal precancerous in:
1-Squamous cell hyperplasia: We observe an increased cell proliferation that can affect the level cell carcinoma of the skin, in this case we speak of Acanthosis, or prebasali or basal layers; the architecture is smooth and lacks atypia
2-Mild dysplasia: architectural alteration accompanied by atypia, limited to the lower third of the epithelium
3-Moderate dysplasia: interesting architectural alteration the middle third of the epithelium, with prominent nucleoli and nuclear abnormalities presenting cells, no abnormal mitosis. The lesions may be associated with Actinic
4-Severe dysplasia: interesting more than two-thirds of the epithelium, with prominent architectural anomalies, atypia, obvious nuclear abnormalities, loss of maturation, nuclear pleomorphism, bizarre nuclei. We observe an increased number of mitosis. Severe dysplasia has the same risk of developing invasive carcinoma of carcinoma in situ
5-Carcinoma in situ: that is a malignant transformation that does not invade the basement membrane
Thyroid nodules
Thyroid nodules are very common feedback: can be completely harmless or be a thyroid tumor.
If there is a neck palpation thyroid enlargement or perceive a targeted ultrasound should be formation with a study and a thyroid function through blood tests.
L ’ ultrasound makes it easy to distinguish a solid nodule from a Cystic nodule (harmless content).
In the case of a solid nodule you will need to consider its size, the morphology, the vascularization and the presence of other nodules in the thyroid or pathological cervical lymph nodes. These parameters will help the clinician to conclude whether a utility ’ cell collection from nodule by ultrasound-guided needle aspiration (FNAC): with a thin needle will some cells will aspire to be analyzed.
Continue reading
Fiberoptic in evaluating dysphagia
Dysphagia, that is the difficulty in swallowing foods, can have many causes and may be caused by an obstacle or laryngopharyngeal level or oesophageal.
L ’ Otolaryngologist plays an important role in the evaluation of dysphagic patients, both in identifying the cause ’ that in ’ food standards setting to minimize risks due to dysphagia. In fact dysphagic patients have a higher risk of inhalation of foods: If swallowing is not effective foods may accidentally penetrate the Airways. L ’ inaction can cause serious lung infections.
The standard fiberoptic allows to evaluate l ’ Anatomy and the correct capacity of the larynx to prevent food from entering the trachea.
Also you can see the pharynx and larynx in real time while the patient ingests liquid foods and semi-solid colored. In this way you can have a clear idea of the level of dysphagia and introduce measures to minimise the risk of pneumonia.
Fiberoptic in the assessment of snoring
All patients with snoring and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) should conduct an assessment ORL with fiberoptic.
In patients with snoring is initially made a standard fiberoptic in order to exclude anatomical issues that might affect or cause the pathology (nasal septum deviation, hypertrophy of lingual base, Palatal PTOSIS)
Then it is important to perform the maneuver of Muller: It requires the patient to a ’ forced inspiration keeping my mouth shut and nostrils plugged. The negative pressure that is created in the pharynx simulates pharyngeal collapse that occurs in sleep with reduced muscle tone.
This procedure allows to simulate, non-invasively, the collapse of the Airways that occurs during sleep.
Identify the anatomical problem that can affect your snoring can be set with the patient proper treatment plan
Food standards and lifestyles to reduce gastroesophageal reflux and reflux laringopatia
Below you can find some important rules to reduce gastroesophageal reflux and reflux and symptoms related to laringopatia. Respecting these rules, you can reduce the discomfort related to disease and even reduce or stop drug therapies. Continue reading
Fiberoptic
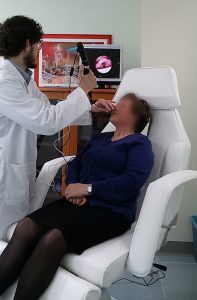 The non-invasively fibroscopy is an examination, Quick, generally well tolerated by the patient that lets you explore the nasal cavities, the pharynx and larynx.
The non-invasively fibroscopy is an examination, Quick, generally well tolerated by the patient that lets you explore the nasal cavities, the pharynx and larynx.
You can perform on an outpatient basis both for adults and children and lasts for a few minutes.
And’ preferable but not mandatory to l ’ examination between meals; l ’ examination is generally well tolerated, It is not painful and causes only mild discomfort rarely may be necessary to apply the anaesthetic sprays.
The fiberscope is equipped with a thin fiber bundle, able to rotate according to the commands of operator which is introduced through one nostril and allows to observe the nasal vestibule, the nasal cavities, the air gaps, in nasal septum, nasopharyngeal cable, the opening of auditory tube, the presence of adenoid tissue, l ’ oropharynx, l ’ hypertrophy of tongue base, the larynx, the motility of the vocal cords, l ’ hypopharynx.
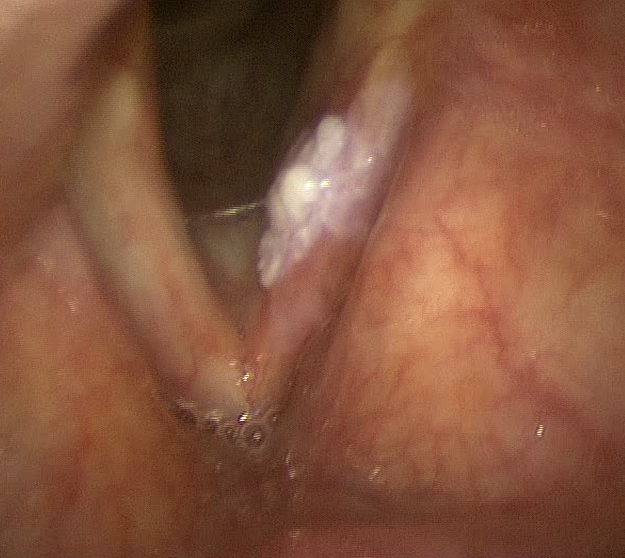
The fiberscope is a key tool for ’ Otolaryngologist who to exclude nasal growths, the pharyngeal and laryngeal. Allows to evaluate the presence of nasal polyps, purulent secretions, sign of sinusitis. In children is the examination of choice to evaluate the adenoid hypertrophy. And’ can also see the vocal cords to study the ’ origin of voice problems (dysphonia), looking for tumors, nodules, polyps, granulomas, Reinke's edema, deficit of motility of the vocal cords. It also has an important role in the evaluation of fiberoptic snoring problems and of the Dysphagia
And’ should make a complicated and if you are having trouble breathing, nasal, chronic sinusitis, epistaxis recurring, effusive persistent otitis media, snoring-sleep apnoea, dysphonia that lasts for more than 15 days, persistent cough without pulmonary problems, appearance of neck Lymphadenopathy.
Transnasal flexible fiberoptic tracheal ranking (possible only in some people very uncooperative)
- « Previous
- 1
- 2
- 3